As the world becomes more interconnected, international events continue to rise.
However, many organisations still face challenges in effectively reaching multilingual audiences, whether at global conferences, academic lectures, policy briefings, or corporate town halls.
The growing global nature of many aspects of life then highlights the need for tools that can broadcast messages seamlessly in multiple languages, ensuring inclusivity and meaningful engagement.
Without a reliable multilingual broadcasting tool, diverse attendees may struggle to follow key presentations, missing out on valuable insights and critical information.
In this article, we’ll learn about multilingual broadcasting—its evolution, how AI is enhancing its accessibility, and how AI-powered multilingual broadcasts actually work.
Let’s dive in!
What is a Multilingual Broadcast?
Broadcasting essentially refers to transmitting audio or video content to a wide audience through various communication mediums, such as radio, television, and now, the Internet.
It is typically one-way communication, with the sender distributing information to multiple recipients at once.
The primary purpose of broadcasting is to disseminate information, educate, entertain, or influence a large audience efficiently.
From public service announcements to live sports and educational content, broadcasting plays a key role in mass communication.
A multilingual broadcast refers to this same process but with content delivered in multiple languages simultaneously to reach diverse, multilingual audiences.

When Did It All Begin?
Historically, the earliest form of broadcasting emerged in the mid-1890s. It started when an Italian electrical engineer, Guglielmo Marconi, found a way to use radio waves to transmit Morse code wirelessly (Whitaker, 2022).
In the early 1950s, television became the primary broadcasting medium, transforming how information and entertainment were delivered to the masses. The evolution continued through the 1960s with pioneering satellite experiments, which led to the rise of Direct Broadcast Satellites (DBS) in the 1980s.
Along with this development, satellite transmission served as the backbone of modern broadcasting. However, while satellite delivery remains in use today, internet-based streaming platforms are gradually displacing it in popularity.
Building on this digital shift, broadcasting has expanded beyond traditional TV and radio. Live streaming, webinars, and virtual events now enable content to be broadcast globally in real-time—often via the Internet.

The Rise of Multilingual Broadcasting
Globalisation, remote work, cross-border collaboration, and the rise of international education have all contributed to increasingly diverse and multilingual audiences.
As events, classes, and conferences increasingly involve international participants, there’s a growing demand for making broadcasts accessible to speakers of different languages.
Relying solely on subtitles or post-event translations often falls short, as delayed delivery can hinder understanding and discourage real-time engagement.
In contrast, real-time multilingual broadcasting allows everyone to follow the message as it unfolds, making it especially valuable for fast-paced settings such as live announcements, global webinars, or international forums.
How AI-Powered Translation Makes Broadcasting More Accessible
The advancement of artificial intelligence can play an important role in breaking language barriers. One of its most powerful contributions is the ability to provide real-time translated captions in multiple languages.
Whether it’s a live conference, a virtual classroom, or a global product launch, AI can instantly generate subtitles that allow diverse viewers to follow the message in the language they’re most comfortable with.
This not only boosts understanding and participation but also ensures that non-native speakers aren’t left behind in fast-paced, information-rich settings..
Besides inclusivity, AI-powered translation offers a more cost-effective solution than traditional human interpretation.
Although live interpreters are highly skilled, their availability, cost, and language coverage can be limited, especially for events involving audiences from multiple language backgrounds.
Broadcasters can use AI to support dozens of languages at once, often with built-in tools that are scalable, efficient, and easy to integrate into existing platforms.
That combination of speed, reach, and affordability redefines what it means to make broadcasting truly global.
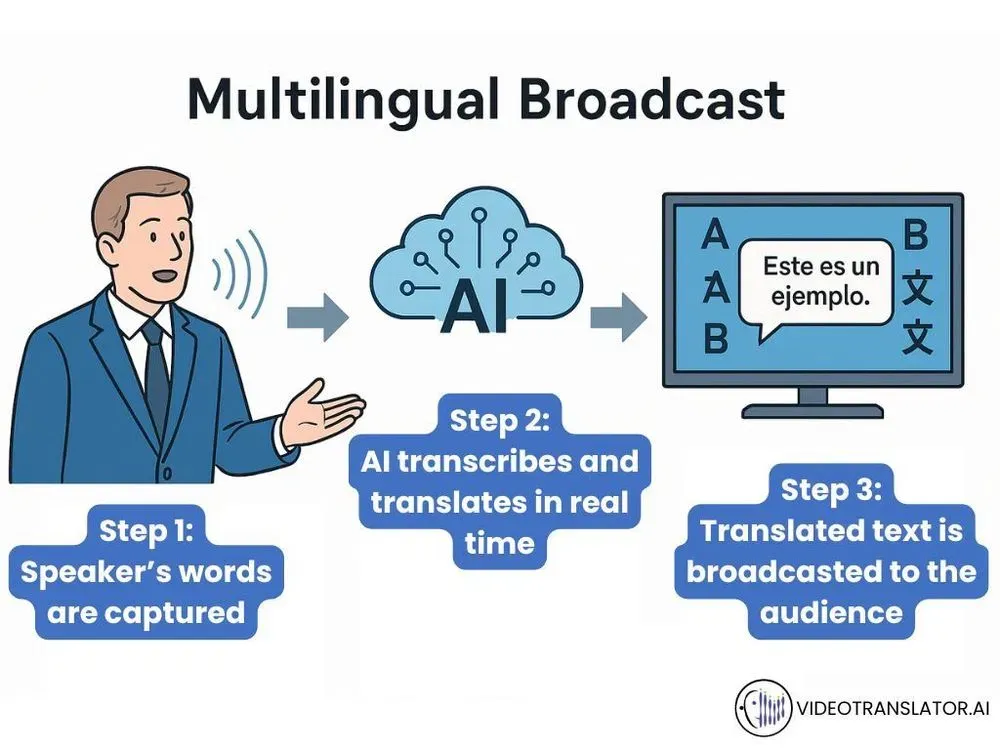
How Does an AI-Powered Multilingual Broadcast Work?
Right after the broadcast starts, the AI begins capturing the speaker’s voice through a microphone. This process is followed by a transcription, where the spoken words are turned into written text.
The AI then quickly translates that text into multiple languages so that viewers can read captions or subtitles in their own language. Some tools are even equipped with voice-overs, aiding those with limited vision.
This whole process happens almost instantaneously, making it easier than ever to include and engage a global audience.
Conclusion
The future of communication is multilingual, and it’s already here. With an AI-powered broadcasting tool, you can share your voice with the world without borders or barriers.
If you have questions regarding a multilingual broadcast tool, feel free to contact us at hello@videotranslator.ai.
VideoTranslatorAI provides a real-time multilingual broadcasting tool that supports over 10 different languages.
Let’s build a more connected, inclusive world with us!