The nurse couldn’t speak a word of Arabic. The patient couldn’t speak English. Twenty years ago, they would have waited hours for an interpreter. Last Tuesday, they had a complete medical consultation in real-time, and neither of them thought twice about it.
AI translation isn’t replacing jobs. It’s quietly rewriting entire careers you interact with every day, and most people haven’t noticed the shift until they’re standing in the middle of it.
Machine-assisted translation now powers 70% of language workflows, but the real story isn’t in the statistics. It’s in the teacher who just communicated with a Mandarin-speaking parent for the first time in three years. It’s in the estate agent closing deals with Korean buyers without hiring an interpreter. It’s in the humanitarian worker building trust in a refugee camp where 12 different dialects are spoken.
Here are seven jobs that are already relying on AI translation, changing how entire industries communicate.
1. Localisation Specialists
From Translators to Cultural Engineers

Here’s a truth: AI translation doesn’t take away from your value as a translator. Rather, it’s a smart way to keep up with the pace of modern work.
Localisation managers used to spend weeks manually translating software interfaces, video games, or mobile apps for different markets.
Now they’re using AI to handle the heavy lifting whilst they focus on what machines can’t do: cultural nuance, humour, slang, and brand consistency.
AI translation surged by 533% in 2024, fundamentally changing how localisation teams work. Instead of translating word-for-word, specialists now review AI-generated drafts and refine them for cultural fit.
For example, when a game character says “That’s sick” in English, AI might translate it literally. The localisation specialist knows it means “amazing” and adjusts accordingly.
Or a software pop-up uses casual American English, they adapt it to match formal German business communication styles.
This highlights that human specialists didn’t disappear. They evolved into cultural engineers who ensure AI translations don’t accidentally insult markets worth millions.
Also read: Why Translation Work is Oddly Satisfying And What It Means for the Language Services Industry
2. Technical and Content Writers
First Drafts at Lightning Speed

Documentation teams producing help centre articles, user manuals, or blog posts in multiple languages used to maintain separate writers for each market.
Now they’re leveraging AI for instant first drafts whilst human editors ensure accuracy and brand voice.
The average translator’s productivity increased by 60% with AI tools like Smartcat; however, the real shift lies in how teams structure their workflow.
For example, a technical writer at a SaaS company writes documentation in English. AI generates versions in Spanish, French, German, and Japanese within minutes. (I wrote something about this few months ago, click here to read the article!
Human editors in each market review for technical accuracy, terminology consistency, and readability.
What used to take weeks now takes days. What used to require five separate writers now requires one writer plus regional editors.
The cost savings are massive, but more importantly, products launch globally faster because documentation doesn’t bottleneck release schedules.
The role evolved from “write content” to “orchestrate multilingual content production whilst maintaining quality across markets.”
Also read: The Great Democratisation of Translation
3. Healthcare Workers
Patient Care Without Language Barriers

I’ve seen this transformation firsthand. Last year, our team, VideoTranslatorAI collaborated with the South Western Sydney Local Health District (SWSLHD) through the NSW Small Business Innovation and Research (SBIR) Program to develop real-time translation tools specifically for healthcare settings.
A midwife treating a patient who speaks only Arabic used to rely on family members to interpret, risking miscommunication about labour complications, medications, or allergies. Now she uses real-time AI translation during telehealth consultations to communicate directly.
“Are you experiencing any bleeding?” The patient hears it in Arabic, responds, and the midwife sees the English translation instantly.
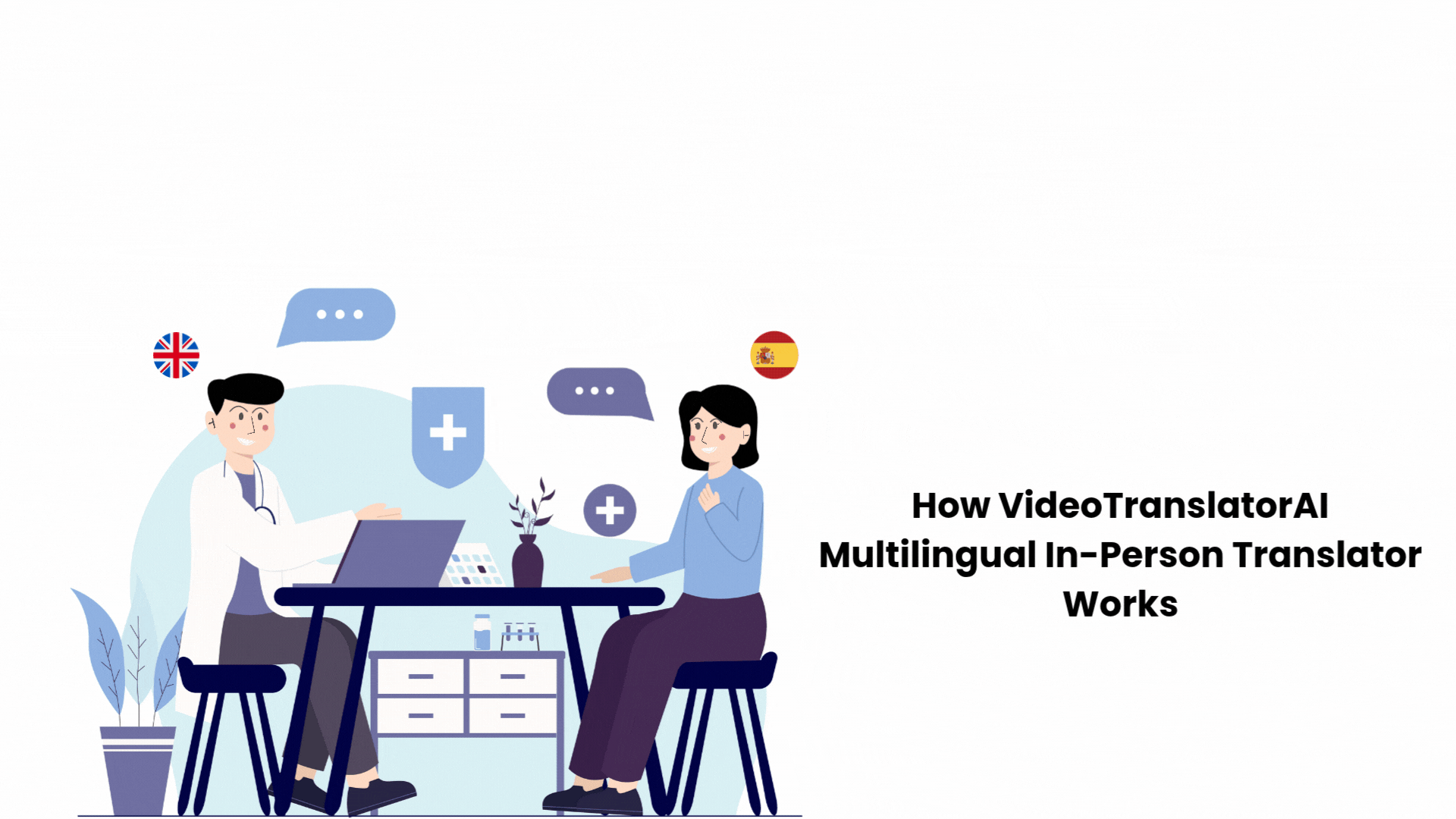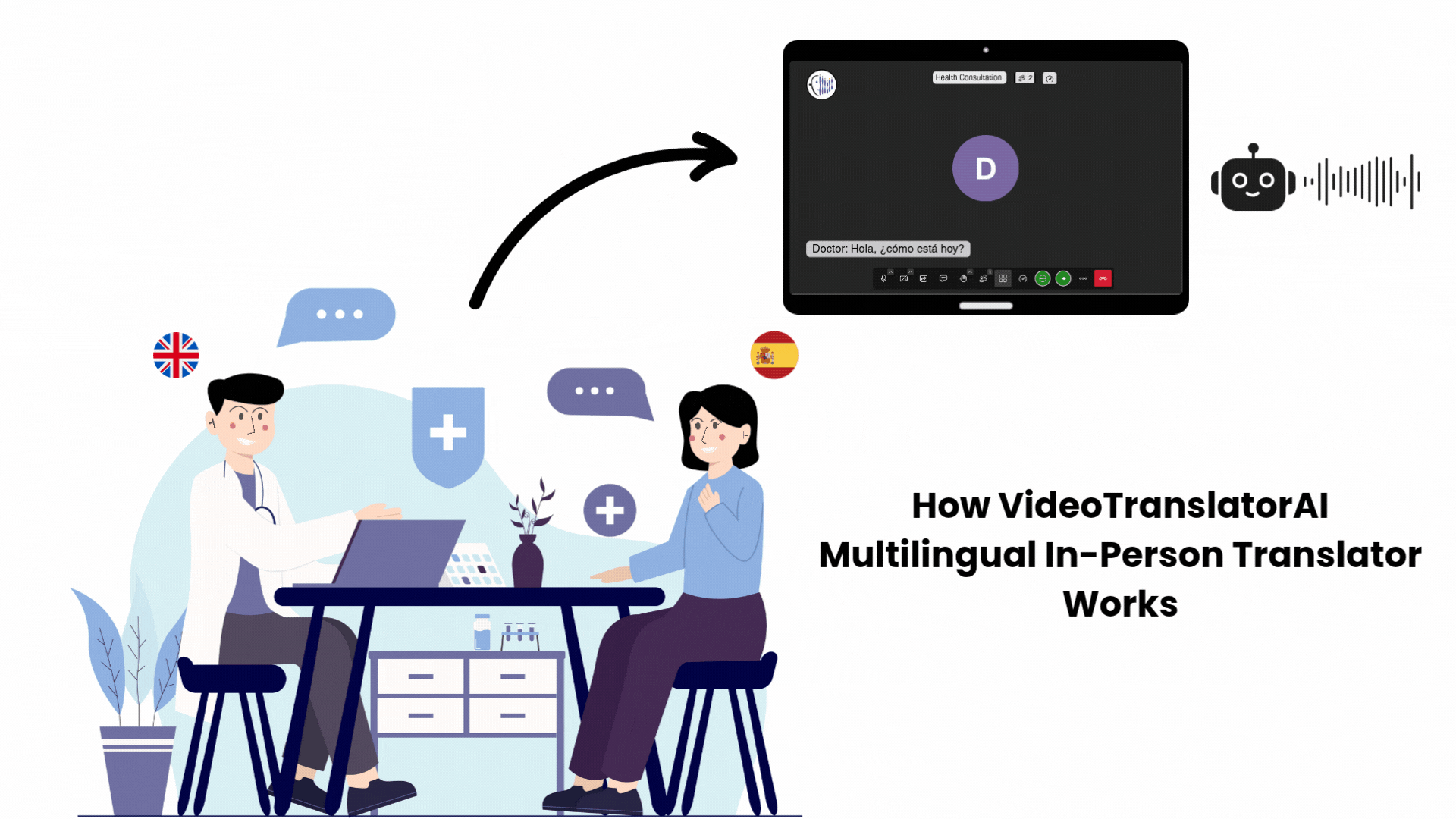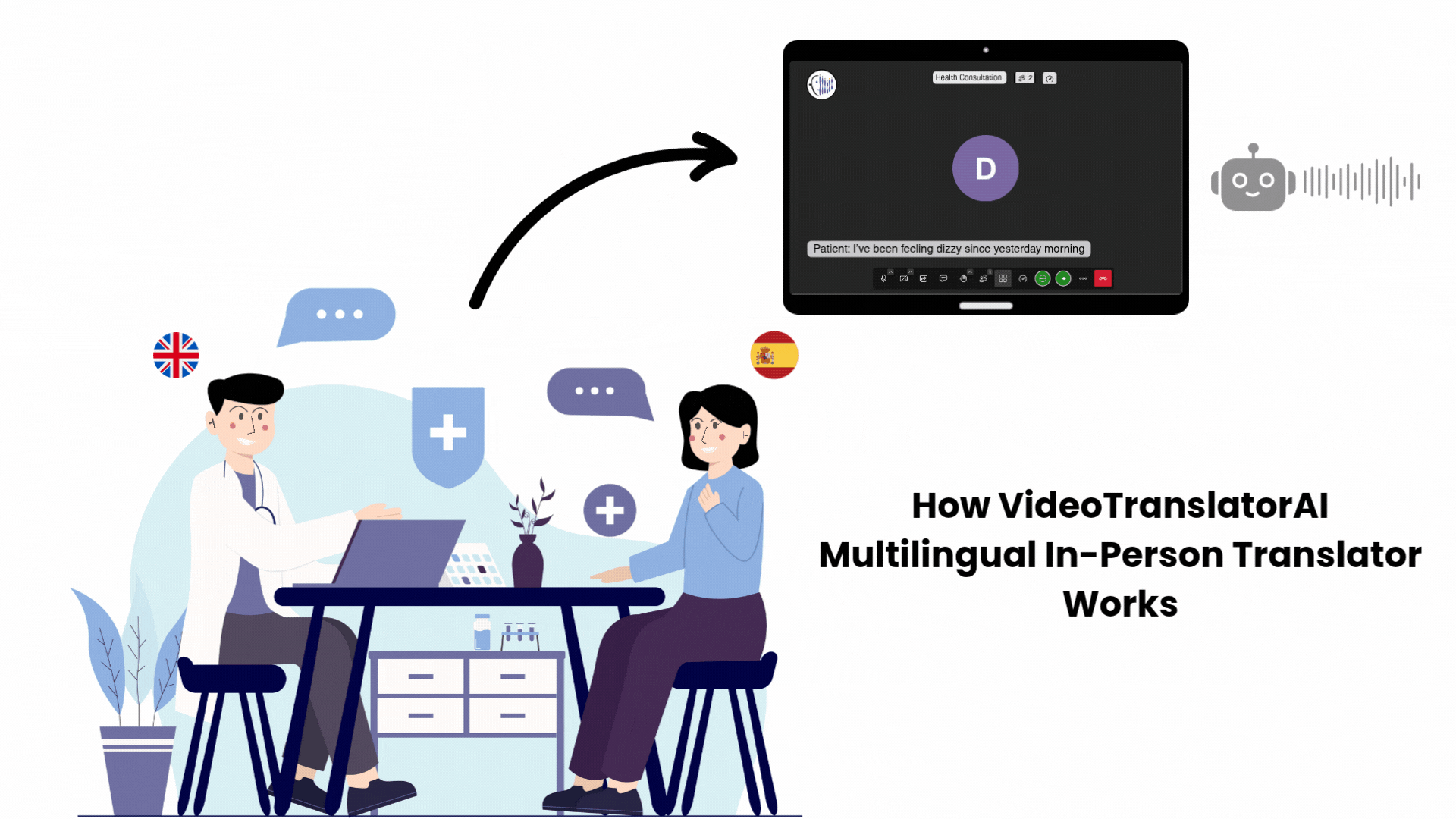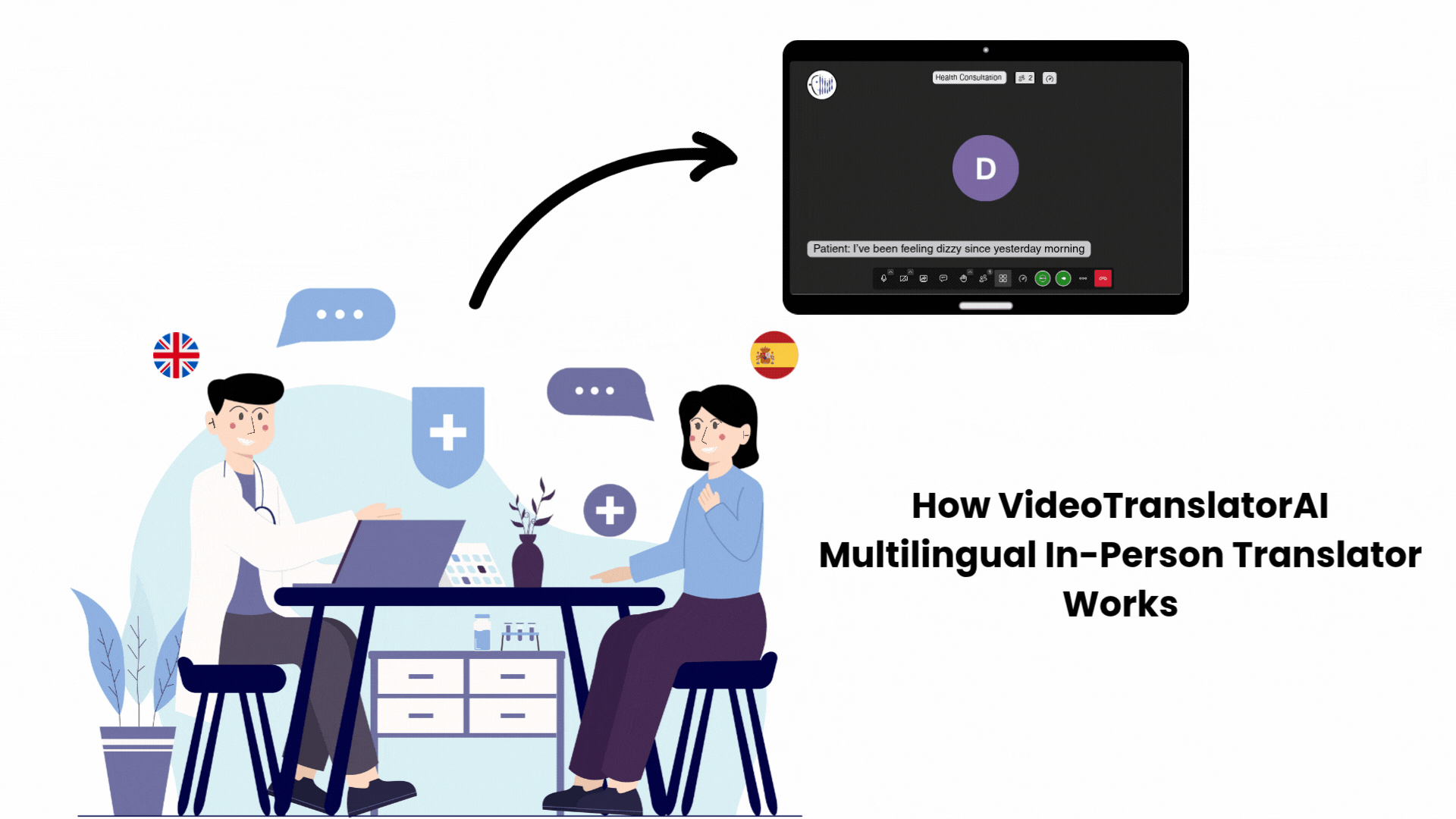
Critical information flows without delay, without relying on untrained interpreters, without risking life-threatening misunderstandings during time-sensitive obstetric care.
Healthcare AI localisation has reduced medical translation errors by 35% compared to manual processes, and hospitals are seeing measurably better patient outcomes when language barriers don’t delay care.
We’re also building video translation capabilities so health communication staff can translate existing patient education videos into culturally and linguistically diverse (CALD) languages. Discharge instructions, medication guidance, and pre-operative preparation videos all become accessible in patients’ native languages.
The profession shifted from “treat patients who speak your language or find an interpreter” to “treat any patient, communicate clearly, ensure safety regardless of language.” And healthcare systems are actively investing in making this the standard, not the exception.
Also read: When Words Fail: How AI Translation is Closing Language Gaps in Healthcare
4. Customer Support Representatives
One Team, Global Reach

Real-time translation apps supported 25% of customer service interactions in 2023, and 40% of live customer support interactions now rely on AI real-time translation.
Companies used to hire separate support teams for each language market. A customer in Brazil got help from Brazilian agents. A customer in Japan reached Japanese support staff.
Expensive, slow to scale, and limited to business hours in each timezone.
Now, a centralised English-speaking support team can use real-time AI translation to communicate with customers globally. An agent in Dublin can help a customer in Seoul without speaking Korean.
The conversation flows naturally because AI translates both sides in real-time.
The job transformed from “speak multiple languages” to “solve problems effectively whilst AI handles linguistic conversion.”
Also read: Customer Service Beyond Borders: Break Language Gaps for Global Clients
5. Teachers and Educators
Breaking Classroom Language Barriers

Let me tell you a real story of my colleague.
A primary school teacher in Sydney has three students who speak Mandarin at home, two who speak Arabic, and one whose family speaks Vietnamese.
Previously, she’d struggled to communicate with parents during conferences or send home important notices.
Now she uses AI translation for real-time subtitles during parent-teacher meetings, translates permission slips instantly, and even broadcasts lessons with multilingual captions for students still developing English fluency.
AI translation solutions processed over 1 billion e-learning course translations in 2022, making education accessible to students regardless of their first language.
The transformation isn’t just about convenience. It’s about inclusion. Students whose parents can’t speak English no longer fall through communication gaps. Teachers can engage with every family, not just the ones who speak the dominant language.
The role expanded from “teach curriculum” to “create inclusive learning environments where language isn’t a barrier to education.”
Also: AI Multilingual Solutions for a Borderless Classroom
6. Humanitarian and Aid Workers
Life-Saving Communication in Crisis Zones

NGOs working in crisis zones face dozens of local dialects, shifting populations, and zero time to find interpreters. When disaster strikes, communication delays cost lives.
Aid workers now use AI interpreters to communicate instantly with displaced communities, building trust fast in situations where every minute matters.
A medical team assessing refugee camp needs can speak to arrivals from multiple regions without waiting for human translators.
The technology isn’t perfect. Dialect variations, technical terms, and emotional nuance still challenge AI systems.
But when you need to communicate “where does it hurt” or “are you allergic to any medications” to someone who speaks a language you’ve never encountered, imperfect real-time translation beats perfect translation that arrives too late.
The job evolved from “work where interpreters are available” to “work anywhere, communicate with anyone, save more lives.”
Also read: Unlocking Humanitarian Aid Through Language Access
7. Real Estate Agents
Closing Global Deals Locally

International buyers are flooding property markets worldwide.
Chinese investors buying Australian property. Middle Eastern buyers interested in London real estate. European retirees purchasing homes in Southeast Asia.
Real estate agents who previously relied on hiring interpreters for showings or sending contracts to translation services are now using AI to communicate in real-time with international clients (Just search for “real estate AI translator” on Google, and you’ll come across a ton of options!)
Agents who embrace AI translation expand their potential client base from “English speakers in my city” to “anyone globally interested in properties I represent.”
The competitive advantage is enormous in markets where international investment drives prices.
The career evolved from “serve local buyers who speak my language” to “serve global clients and compete internationally from your local market.”
The Pattern You Need to See
Notice what these jobs have in common? They’re not tech roles. They’re jobs you encounter regularly: teachers, nurses, customer service agents, estate agents.
The AI translation revolution isn’t happening in Silicon Valley labs.
It’s happening in classrooms, hospitals, call centres, and refugee camps. It’s reshaping careers you interact with every week, often without you noticing.
The professionals in these roles aren’t being replaced. They’re being empowered to serve populations they couldn’t reach before.
A monolingual teacher now supports multilingual students. A single-language support team now helps global customers. An aid worker communicates in crisis zones with dozens of dialects.
What This Means for Communication
As someone building real-time translation systems for international meetings, I see this pattern clearly: AI translation works best when it augments human expertise rather than replacing it.
The localisation specialist still needs cultural knowledge. The teacher still needs pedagogical skill. The healthcare worker still needs medical training. The estate agent still needs negotiation expertise.
What changed is that language barriers no longer limit who these professionals can serve. The technology removes friction, expands reach, and enables work that was previously impossible without multilingual staff or expensive interpretation services.
The future isn’t “AI replaces translators.”
It’s “AI lets everyone communicate across languages whilst experts focus on expertise, not linguistic conversion.”
Your job might be next. And that’s not a threat. It’s an opportunity to serve populations you couldn’t reach before, compete in markets previously closed to you, and make impact beyond linguistic boundaries that once felt permanent.
The revolution is here. It’s just distributed across everyday jobs instead of concentrated in headlines.
If you’re ready to expand your reach through seamless multilingual communication or need to translate your media (audio or video) for global audiences, explore VideoTranslatorAI or contact us at hello@videotranslator.ai.